Microwave Disgester
Introducing the latest addition to our line of innovative laboratory equipment – the Microwave Digester! This cutting-edge microwave digester is designed to streamline and enhance your sample preparation process with precision and efficiency. Say goodbye to time-consuming traditional digestion methods and hello to rapid, accurate results with our Digestor de Microondas. Whether you are working in environmental analysis, food testing, or any other laboratory application, this instrument is a game-changer in simplifying complex digestion procedures.
Equipped with advanced features and user-friendly controls, the Digestor de Microondas offers unmatched convenience and reliability in your lab workflow. Its robust construction ensures durability and long-lasting performance, making it a valuable asset for your research and analytical needs. Experience the benefits of accelerated digestion times and improved sample throughput with our top-of-the-line Digestor de Microondas – the ultimate solution for modern laboratories seeking optimized processing and consistent results.

MICROWAVE DISGESTER KALSTEIN
At Kalstein you can find the ideal Microwave Disgesters for Your Laboratory

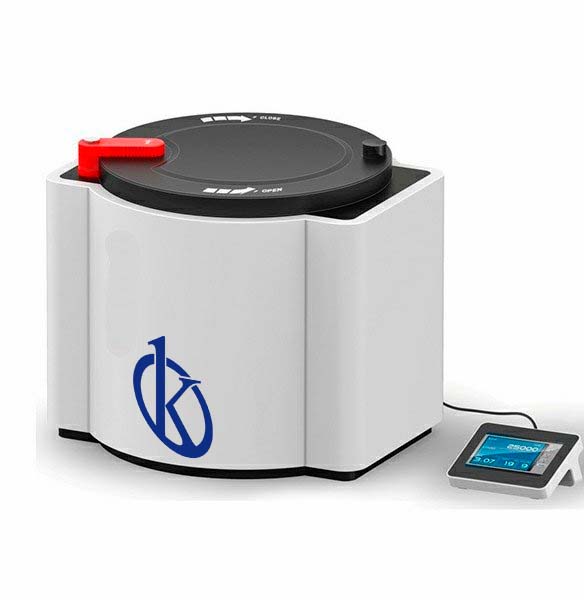
Microwave Digestion System YR04959 // YR04960
Special Designed Sample Digestion Vessel The automatic vent and self-resealing structure which won national patent ensures the digestion vessels can automatical...
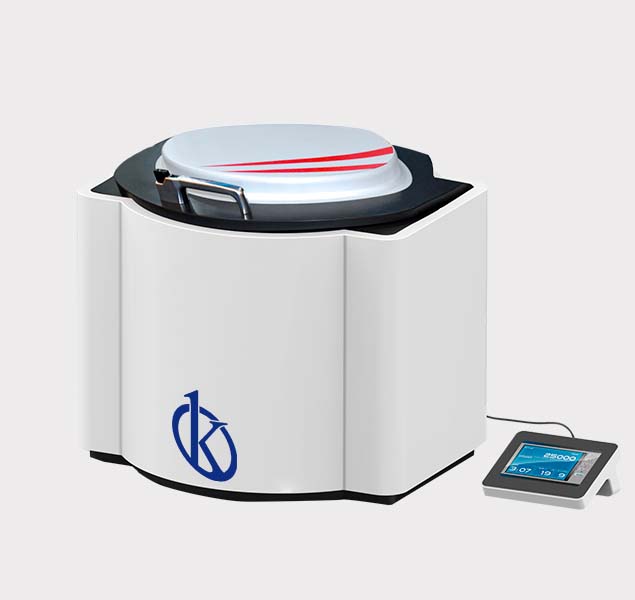

Microwave Digestion System YR04957 // YR04958
Special Designed Sample Digestion Vessel. The automatic vent and self-resealing structure which won national patent ensures the digestion vessels can automatical...

Microwave Digestion System YR04953 // YR04956
YR04953 // YR04956 series is a new designed microwave digestion system. Different from the previous model series is newly designed and fully upgraded with high...
Our Microwave Disgester best seller
YR04953 // YR04956 series is a new designed microwave digestion system. Different from the previous model series is newly designed and fully upgraded with higher performance and safer protection system.
The smart design and perfect performance make it warmly welcomed by users worldwide.
Features
Optional vessel quantity, up to 12 vessels to meet different digestion requirements.
Vertical design for even distribution of microwave.
Real-time monitoring for both temperature and pressure of each vessel.
Contactless sensor monitoring with no burst disk design saves consumables cost and maintenance cost.
Imported vessel material for both sample vessel and protection vessel highly ensures safety.
7 inch color Touch screen with user-friendly interface for easy operation.
Imported CFRP outer shell material with high strength ensures impact resistance.
Pre-installed general standard methods, users can also create, save, modify and delete the method.
316L industrial stainless steel tank with multilayer teflon coating avoids acid corrosion, also improved cooling efficiency.
| Model | YR04953 | YR04954 | YR04955 | YR04956 |
| Vessel Quantity | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
| Temperature Monitoring System | Contactless IR Sensor Temperature Monitoring | |||
| Each Vessel Temperature Controlled | ||||
| Temperature Controlling Range: 50~400℃ | ||||
| Temperature Accuracy: ±0.1℃ | ||||
| Display Accuracy: ±0.1℃ | ||||
| Pressure Monitoring System | Contactless Sensor Pressure monitoring | |||
| Each Vessels Pressure Controlled | ||||
| Pressure Controlling Range: 0~15MPa | ||||
| Pressure Accuracy: ±0.01MPa | ||||
| Display Accuracy: ±0.01Mpa | ||||
| Vessel Volume | 100mL | |||
| Sample Vessel | Imported TFM | |||
| Material | ||||
| Rotation | One Direction 360° continuous rotating | |||
| Microwave Tank | 316L stainless steel tank with corrosion-proof coating | |||
| Microwave Power | 0-1000W (Adjustable) | |||
| Microwave Leakage | <5mw/cm2 | |||
| Air Exhaust | High power corrosion-proof air blower | |||
| Power | AC 220V±10%, 10A, 50/60Hz | |||
| Dimension | 490×560×630mm(L×W×H) | |||
| Weight | 47KG | |||
| Display | 7 inch Touch Screen | |||
| Protection Vessel Material | Peek+Glass Fiber | |||

Analysis of the best Microwave Disgesters for Your Laboratory

What is a Microwave Digester?
They are equipment that has a digestion system, which is used to mineralize solid samples from which we want to obtain reliable information at elemental level, a spectroscopic technique is used, and requir...

Microwave digester: in which scientific sectors is it used?
The use of this equipment for different scientific processes is proven thanks to the scientific researchers in the areas of chemistry and engineering, where the use ...

What is Acid Digestion for Metal Determination?
Using atomic absorption spectrometry techniques and microwave digesters, traditional methods for acid digestion are followed, and they are used for developi...

How to Ensure Food Quality with the Microwave Digester
Microwave digesters are equipment that perform sample digestion in order to obtain information about its components at the elementary level, they are used in ma...
Catalog of models of Microwave Disgesters on offer
KALSTEIN UPDATED
Guidelines for you to become an expert in Microwave Disgesters
The Microwave Disgester equipment are essential products in Your Laboratory, we provide you with guidance and recommendations for a better use, so you can work like an expert.
What is a microwave digester used for?
How is the Digestion of a Sample done?
Microwave Digester: how does it work?
Microwave Digestion System in Tumor Samples to Detect Cancer

Frequently asked questions from our customers about Microwave Disgesters
To know the price of the microwave disgesters we invite you to send us an email with your request using the contact form. HERE
The delivery time of your Kalstein product will depend on the following:
- Whether the equipment you are interested in is in stock or if it needs to be manufactured.
- The type of freight you have chosen, which can be either air or sea.
- Equipment in stock:
– Delivery Time (Air): 15-30 days.
– Delivery Time (Sea): 45-60 days.
- Equipment not in stock:
– Delivery Time (Air): 30-60 days.
– Delivery Time (Sea): 60-90 days.
You can make your purchase through:
- By email: [email protected]
- By phone: +33 (0) 1 70 39 26 50
- Online shopping: Through the official Kalstein website in your country.
At Kalstein, we provide our customers with inductions and technical support through new online methods. You can visit our induction videos, technical assistance, and guidance provided by a Kalstein team through our Youtube channel (Kalstein English). HERE
Send us a direct message and one of our agents will contact you
Microwave Disgester
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed dignissim placerat mauris cursus laoreet. Nam feugiat lacus ex, at fermentum sapien accumsan nec. Curabitur auctor porttitor mi non malesuada. Aenean condimentum, purus vitae rhoncus imperdiet, justo eros aliquam ipsum, at egestas leo diam eget libero.

Catalog of models of Microwave Disgester on offer.
-

Hematology Analyzer For Veterinary YR05122-V
-
ECG Monitor 12 Channel Portable ECG Equipment YR05162
-

Electric Heating Drying Oven YR06446
-
Mini Centrifuge With Large Capacity YR012G
-

Intelligent Electric Wheelchair YR06432
-

Manual Wheelchair With Spray Function YR06431
-

Laminar Flow Cabinet YR06430 // YR06430-1
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Counter Pressure Steam Autoclave YR06424// YR06429
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Pulsating Vacuum Autoclave With Printer YR06418 // YR06423
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

POCT Consumables Strips YRA404
-

Substrate YRA402
-

System Washing Solution YRA401
-

Reaction Cuvette YRA400
-

Diabetes Test YRA399
-

Allergy Test YRA398
-

Anemia Test YRA395 // YRA397
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Descubre más de nuestro catálogo
Tipos de Microwave Disgester

[Producto] A
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

[Producto] B
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Find out more about Microwave Disgester with our guides.
Children’s Wheelchair YR05460: Innovative Design and Technical Features
Product Description The Children's Wheelchair YR05460 represents a significant advancement in mobility solutions for young users, combining technical precision with...
Enhancing Mobility: Advanced Features of Children’s Wheelchair YR05459
Product Description The Children's Wheelchair YR05459 is a cutting-edge mobility solution specifically designed to cater to the needs of children...
Innovative Electric Stair Climbing Wheelchair YR05446: Ultimate Mobility Solution
Product Description The Electric Stair Climbing Wheelchair YR05446 represents a significant leap forward in mobility assistance technology. Designed to enhance...




